Neuropeptides
Volume
38, Issues 2-3 , April-June 2004, Pages 98-105

doi:10.1016/j.npep.2004.04.004 
Copyright
© 2004 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Hyperglycemia induced by acute central fluoxetine administration: role of the
central CRH system and 5-HT3 receptors
F. Carvalhoa,
D. Barrosa,
J. Silvaa,
E. Rezendea,
M. Soaresb,
J. Fregonezeb
and E. De Castro e Silva ,
,  , b
, b
a Life Sciences Department, Bahia
State University, 41195-001 Salvador, Bahia, Brazil
b Department of Physiology, Health Sciences Institute,
Federal University of Bahia, 40110-100 Salvador, Bahia, Brazil
Received
26 December 2003; accepted 19 April 2004. Available online 17 June
2004.
Abstract
Brain serotonin and CRH systems participate in the control of blood glucose
levels. We have previously demonstrated that the pharmacological stimulation of
central 5-HT3 receptors, the target for several therapeutic agents
used as antiemetics in the course of chemotherapy, induces hyperglycemia. The
aim of the present study was to investigate the participation of the brain CRH
component and 5-HT3receptors in basal blood glucose levels as well as
in the hyperglycemia induced by third ventricle injections of fluoxetine, a
serotonin reuptake inhibitor with a broad range of clinical use. In this study,
we used fasted adult Wistar male rats (220 ± 20 g) whose third
ventricles were cannulated 7 days prior to the experiments. Acute third
ventricle injections of fluoxetine caused a significant increase in plasma
glucose levels throughout the experiment. Pretreatment with 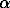 -helical
CRH, a selective CRH antagonist, significantly blunted fluoxetine-induced
hyperglycemia. Also, pretreatment with two distinct selective 5-HT3
receptor antagonists (LY-278,584 and ondansetron) significantly impaired the
rise in plasma glucose levels observed in fluoxetine-treated animals pretreated
with isotonic saline solution. None of these antagonists was able to modify
blood glucose levels when injected alone into the third ventricle. Animals
receiving third ventricle injections of fluoxetine, in spite of being
hyperglycemic, presented plasma insulin levels similar to those displayed by
normoglycemic, saline-treated controls. It is suggested that the acute increase
in brain serotonergic activity caused by third ventricle injections of
fluoxetine induces a hyperglycemic response that requires the functional
integrity of the brain CRH system and 5-HT3 receptors. Also, it is
proposed that the absence of a compensatory increase in plasma insulin levels
may contribute to the generation of a hyperglycemic response after central
fluoxetine administration.
-helical
CRH, a selective CRH antagonist, significantly blunted fluoxetine-induced
hyperglycemia. Also, pretreatment with two distinct selective 5-HT3
receptor antagonists (LY-278,584 and ondansetron) significantly impaired the
rise in plasma glucose levels observed in fluoxetine-treated animals pretreated
with isotonic saline solution. None of these antagonists was able to modify
blood glucose levels when injected alone into the third ventricle. Animals
receiving third ventricle injections of fluoxetine, in spite of being
hyperglycemic, presented plasma insulin levels similar to those displayed by
normoglycemic, saline-treated controls. It is suggested that the acute increase
in brain serotonergic activity caused by third ventricle injections of
fluoxetine induces a hyperglycemic response that requires the functional
integrity of the brain CRH system and 5-HT3 receptors. Also, it is
proposed that the absence of a compensatory increase in plasma insulin levels
may contribute to the generation of a hyperglycemic response after central
fluoxetine administration.
Author Keywords: Serotonin; CRH; 5-HT3 receptors;
LY-278,584; Ondansetron; Insulin; Hyperglycemia; Fluoxetine; 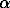 -Helical
CRH
-Helical
CRH

 Corresponding author. Present address: Departamento de
Fisiologia, Instituto de Ciências da Saúde, Universidade Federal da Bahia,
40110-100 Salvador, Bahia, Brasil. Tel.: +55-71-235-7518; fax: +55-71-337-0591
Corresponding author. Present address: Departamento de
Fisiologia, Instituto de Ciências da Saúde, Universidade Federal da Bahia,
40110-100 Salvador, Bahia, Brasil. Tel.: +55-71-235-7518; fax: +55-71-337-0591
















 ,
,  , b
, b
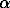 -helical
CRH, a selective CRH antagonist, significantly blunted fluoxetine-induced
hyperglycemia. Also, pretreatment with two distinct selective 5-HT3
receptor antagonists (LY-278,584 and ondansetron) significantly impaired the
rise in plasma glucose levels observed in fluoxetine-treated animals pretreated
with isotonic saline solution. None of these antagonists was able to modify
blood glucose levels when injected alone into the third ventricle. Animals
receiving third ventricle injections of fluoxetine, in spite of being
hyperglycemic, presented plasma insulin levels similar to those displayed by
normoglycemic, saline-treated controls. It is suggested that the acute increase
in brain serotonergic activity caused by third ventricle injections of
fluoxetine induces a hyperglycemic response that requires the functional
integrity of the brain CRH system and 5-HT3 receptors. Also, it is
proposed that the absence of a compensatory increase in plasma insulin levels
may contribute to the generation of a hyperglycemic response after central
fluoxetine administration.
-helical
CRH, a selective CRH antagonist, significantly blunted fluoxetine-induced
hyperglycemia. Also, pretreatment with two distinct selective 5-HT3
receptor antagonists (LY-278,584 and ondansetron) significantly impaired the
rise in plasma glucose levels observed in fluoxetine-treated animals pretreated
with isotonic saline solution. None of these antagonists was able to modify
blood glucose levels when injected alone into the third ventricle. Animals
receiving third ventricle injections of fluoxetine, in spite of being
hyperglycemic, presented plasma insulin levels similar to those displayed by
normoglycemic, saline-treated controls. It is suggested that the acute increase
in brain serotonergic activity caused by third ventricle injections of
fluoxetine induces a hyperglycemic response that requires the functional
integrity of the brain CRH system and 5-HT3 receptors. Also, it is
proposed that the absence of a compensatory increase in plasma insulin levels
may contribute to the generation of a hyperglycemic response after central
fluoxetine administration.
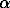 -Helical
CRH
-Helical
CRH ![]()
 Corresponding author. Present address: Departamento de
Fisiologia, Instituto de Ciências da Saúde, Universidade Federal da Bahia,
40110-100 Salvador, Bahia, Brasil. Tel.: +55-71-235-7518; fax: +55-71-337-0591
Corresponding author. Present address: Departamento de
Fisiologia, Instituto de Ciências da Saúde, Universidade Federal da Bahia,
40110-100 Salvador, Bahia, Brasil. Tel.: +55-71-235-7518; fax: +55-71-337-0591