 |
 |
|
Home | Current Issue |
Past
Issues | Search | Collections
| PDA Services | Subscribe | Contact Us | Help | ACP Online
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
7 March 2000 | Volume 132 Issue 5 | Page 417
On 15 April 1999, a 78-year-old man was admitted to our hospital
with icteric acute hepatitis. His medical history revealed Parkinson
disease that was being treated with levodopa and pergolide and
a major depression episode that had been treated with
electroconvulsive therapy 2 months before admission. On 6 March, he
had begun receiving venlafaxine at an initial dosage of 37.5 mg/d;
this was increased to 150 mg/d on 9 April. Abdominal
ultrasonography showed no anatomic abnormalities. In sharp contrast
to his previous normal liver chemistry analysis, his liver function
at admission showed the following abnormalities: alanine
aminotransferase level, 3.97 µkat/L (normal < 1.08
µkat/L); aspartate aminotransferase level, 4.36 µkat/L
(normal < 0.62 µkat/L); 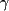 -glutamyltransferase level,
12.17 µkat/L (normal < 1.42 µkat/L); alkaline
phosphatase level, 11.33 µkat/L (normal < 2.27
µkat/L); total bilirubin level, 87 µmol/L
(normal < 17.1 µmol/L); and direct bilirubin level, 86
µmol/L (normal < 5.5 µmol/L). Serologic tests for
hepatitis A, B, and C yielded negative results.
-glutamyltransferase level,
12.17 µkat/L (normal < 1.42 µkat/L); alkaline
phosphatase level, 11.33 µkat/L (normal < 2.27
µkat/L); total bilirubin level, 87 µmol/L
(normal < 17.1 µmol/L); and direct bilirubin level, 86
µmol/L (normal < 5.5 µmol/L). Serologic tests for
hepatitis A, B, and C yielded negative results.
While venlafaxine therapy was progressively discontinued (the patient still received his regular therapy), the patient’s health gradually improved. This improvement is supported by the fact that his liver function test results returned to normal within 5 weeks.
We conclude that it is well justified to identify venlafaxine as the culprit in the patient’s acute liver toxic insult. We excluded all other possible causes of toxic hepatic injury, and liver function returned to normal after discontinuation of venlafaxine therapy. We concur with Horsmans and colleagues and strongly support their recommendation that patients taking venlafaxine be regularly monitored for liver function.
| Author
and Article Information
|
|---|
| Reference
|
|---|
1. Horsmans Y, De Clercq M, Sempoux C.
Venlafaxine-associated hepatitis [Letter]. Ann Intern Med. 1999;130:944-944.
About Letters
The Editors welcome submissions for possible publication in
the Letters section. Authors of letters should:
Include no more than 300 words of text, three
authors, and five references
Type with
double-spacing
Send three copies of the
letter, an authors' form (see Table of Contents for location) signed by all
authors, and a cover letter describing any conflicts of interest related to the
contents of the letter
Letters commenting
on an Annals article will be considered if they are received within 6 weeks of
the time the article was published. Only some of the letters received can be
published. Published letters are edited and may be shortened; tables and figures
are included only selectively. Authors will be notified that the letter has been
received. If the letter is selected for publication, the author will be notified
about 3 weeks before the publication date. Unpublished letters cannot be
returned.
Annals welcomes electronically
submitted letters. The Internet address is http://www.acponline.org/journals/annals/letters.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||