

|
| |||
| This Document | ||
| Abstract | ||
| Full Text + Links | ||
| PDF (437 K) | ||
|
| ||
| Actions | ||
| E-mail Article | ||
Neuronal cell death induced by antidepressants: lack of correlation with
Egr-1, NF- Pia Bartholomäa,
1,
Nina Erlandssona,
1,
Katrin Kaufmanna,
Oliver G. Rösslera,
Bernd Baumannb,
Thomas Wirthb,
Klaus M. Giehlc
and Gerald Thiel B and
extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase activation
B and
extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase activation
 ,
,  , a
, a
a Department of Medical
Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Saarland Medical Center,
D-66421 Homburg, Germany
b Department of
Physiological Chemistry, University of Ulm, Albert-Einstein-Allee 11, 89081 Ulm,
Germany
c Department of Anatomy, University of
Saarland Medical Center, D-66421 Homburg, Germany
Received 27 November
2001; accepted 28 January 2002. Available online 13 March 2002.
The tricyclic antidepressants (TCA) amitriptyline and desipramine and the
serotonin reuptake inhibitor fluoxetine induce, at  M
concentrations, cell death in HT22 immortalized hippocampal neurons and PC12
pheochromocytoma cells. Here, we show that these neurotoxic effects are
accompanied by a selective activation of extracellular signal-regulated protein
kinase (ERK), the biosynthesis of the transcription factor Egr-1 and an increase
in the transcriptional activity of NF-
M
concentrations, cell death in HT22 immortalized hippocampal neurons and PC12
pheochromocytoma cells. Here, we show that these neurotoxic effects are
accompanied by a selective activation of extracellular signal-regulated protein
kinase (ERK), the biosynthesis of the transcription factor Egr-1 and an increase
in the transcriptional activity of NF- B.
However, an impairment of both ERK activation and Egr-1 biosynthesis by the MAP
kinase kinase-1 (MEK-1) inhibitor PD98059 did not block cell death. Moreover,
stimulation of ERK phosphorylation and Egr-1 biosynthesis by
sphingosine-1-phosphate did not induce cell death, indicating that stimulation
of the ERK signaling pathway and Egr-1 biosynthesis are not required for
neuronal cell death induced by antidepressants. Likewise, attenuation of
antidepressant-induced NF-
B.
However, an impairment of both ERK activation and Egr-1 biosynthesis by the MAP
kinase kinase-1 (MEK-1) inhibitor PD98059 did not block cell death. Moreover,
stimulation of ERK phosphorylation and Egr-1 biosynthesis by
sphingosine-1-phosphate did not induce cell death, indicating that stimulation
of the ERK signaling pathway and Egr-1 biosynthesis are not required for
neuronal cell death induced by antidepressants. Likewise, attenuation of
antidepressant-induced NF- B
activity by elevation of the intracellular cAMP concentration or by retroviral
driven expression of the non-degradable superrepressor I
B
activity by elevation of the intracellular cAMP concentration or by retroviral
driven expression of the non-degradable superrepressor I B
B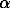 S32A/S36A
demonstrated that the elevation of NF-
S32A/S36A
demonstrated that the elevation of NF- B
activity by amitriptyline, desipramine and fluoxetine is not an integral part of
the apoptotic signaling cascade triggered by these compounds.
B
activity by amitriptyline, desipramine and fluoxetine is not an integral part of
the apoptotic signaling cascade triggered by these compounds.
Author Keywords: Antidepressants; Egr-1; Extracellular
signal-regulated kinase; Neuronal cell death; NF- B;
Sphingosine-1-phosphate
B;
Sphingosine-1-phosphate
Abbreviations: dbcAMP,
N,2'-O-dibutyryladenosine-3:5-cyclic monophosphate; Egr-1, early
growth response 1; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase; IBMX,
isobutyl-1-methylxanthine; MTT,
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide; TCA, tricyclic
antidepressants; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase fluorescein-dUTP
3'-end labeling. ![]()
1 These authors contributed equally to the study.
 Corresponding author. Tel.: +49-6841-1626504; fax:
+49-6841-1626500; email: bcgthi@uniklinik-saarland.de
Corresponding author. Tel.: +49-6841-1626504; fax:
+49-6841-1626500; email: bcgthi@uniklinik-saarland.de
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Volume 63, Issue 8 , 15 April 2002, Pages 1507-1516 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Send feedback to ScienceDirect |